Example if p then q p therefore , q modus ponens ( affirming the consequent ) what argument form is this if its raining , the park is closed the park is not closed therefore, it is not raining example if p, then q not q therefore, not pThis is just the truth table for \(P \imp Q\text{,}\) but what matters here is that all the lines in the deduction rule have their own column in the truth table Remember that an argument is valid provided the conclusion must be true given that the premises are true The premises in this case are \(P \imp Q\) and \(P\text{}\) Both arguments are of course valid What is common between them is that they have the same structure or form If P then Q P Therefore Q Here, the letters P and Q are sentence letters They are used to translate or represent statements By replacing P and Q with appropriate sentences, we can generate the original valid arguments
Which Of The Following Symbolizes A Modus Tollens Chegg Com
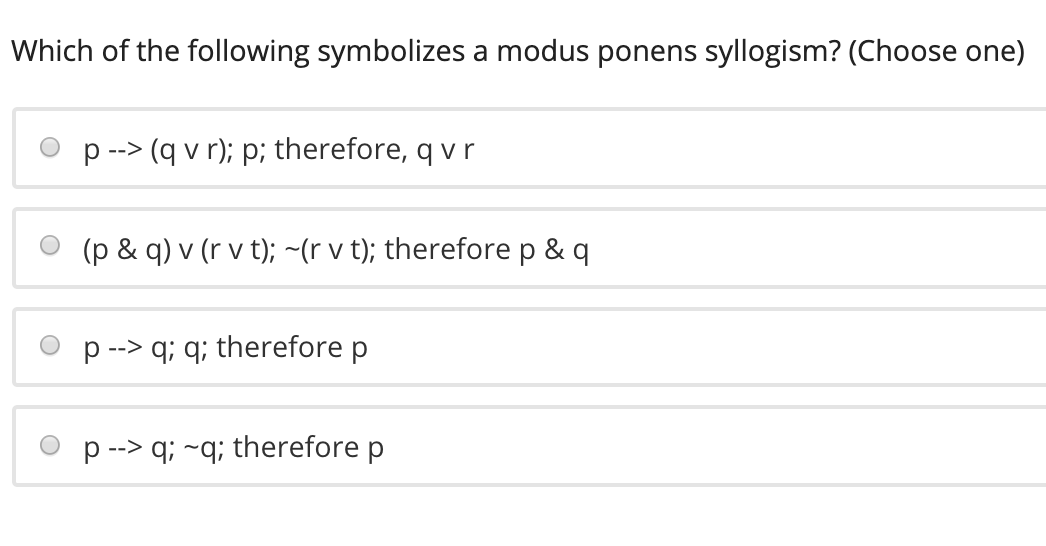
If p then q q therefore p is an example of what kind of common argument
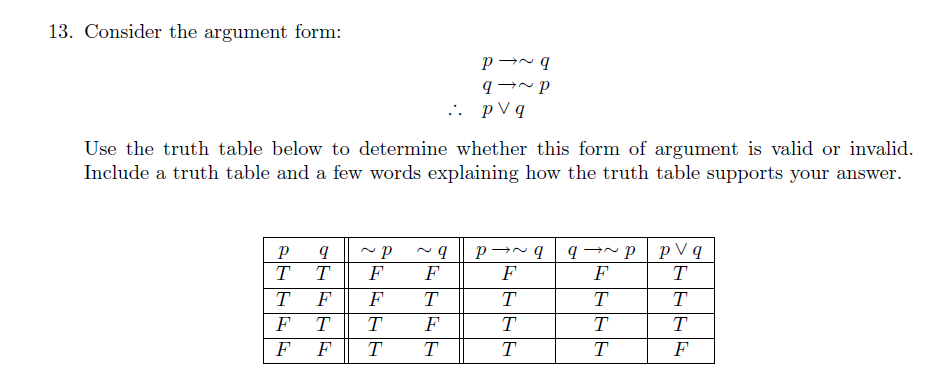
If p then q q therefore p is an example of what kind of common argument-If I have a college degree, then I am not lazy (p →~ q) I don't have a college degree )(~ p Therefore, I am lazy q Hypothesis )((p →~ q)∧~ p Conclusion q Argument in symbolic form (( p →~ q)∧~ p) →q To test to see if the argument is valid, we take the argument in symbolic form and construct a truth tableIt has the form p>q, and q You can't apply this law;




Argument Analysis 7 10
Rule of inference Modus ponens Definition It has the form If p, then q p ∴ q The term modus ponens in Latin means "method of affirming" p q p → q p q T T T T T T F F T F T T F F F T F Example If the sum of the digits of 371,487 is divisible by 3, then 371,487 is divisible by 3 The fallacy of affirming the consequent is any argument of the following form If p, then q;Formal logic Formal logic The propositional calculus The simplest and most basic branch of logic is the propositional calculus, hereafter called PC, so named because it deals only with complete, unanalyzed propositions and certain combinations into which they enter Various notations for PC are used in the literature In that used here the symbols employed in PC first comprise variables
In fact, there is no law that you can apply, soFamous If P, Then Q Logical Argument Example Premise #1 If (P) this rock hits that window, then (Q) that window will break Thus, in the precise specifications of the P/Conditions/Causes and therefore the causes of the Q/Consequence(s)/Effect(s) of an If P, Then Q logical argument we find the basis for true knowledge, the accurateWays in which the propositions may fail to be equivalent Here is another example Example 232 Show (p!q) is equivalent to p^q Solution 1 Build a truth table containing each of the statements p q q p!q (p!q) p^q T T F T F F T F T F T T F T F T F F F F T T F F Since the truth values for (p!q) and p^qare exactly the same for all possible
Consider the argument form If P then Q Not Q Therefore, Not P Is this form modus ponens, affirming the consequent or something else?If p then q;Otherwise it is true The contrapositive of a conditional statement of the form "If p then q " is "If ~ q then ~ p "



Validity Soundness And Valid Patterns




Chapter 22 Common Propositional Argument Forms Introductory Remarks P 2 This Chapter Introduces Some Of The Most Commonly Used Deductive Argument Ppt Download
Therefore p is true Conjunction p,q ∴ (p∧q) p and q are true separately;For example, consider this which includes a fallacy of affirming the consequent "If it is raining the ground will be wet The ground is wet If p then q q Therefore p This kind if argument is also called a CON This is common to get someone to fall for scheme to get moneyBut either not q or not s;




Philosophy Logic And Logical Arguments Ppt Video Online Download



Academic Oup Com Pq Article Pdf 78 26 Pq 0026 Pdf
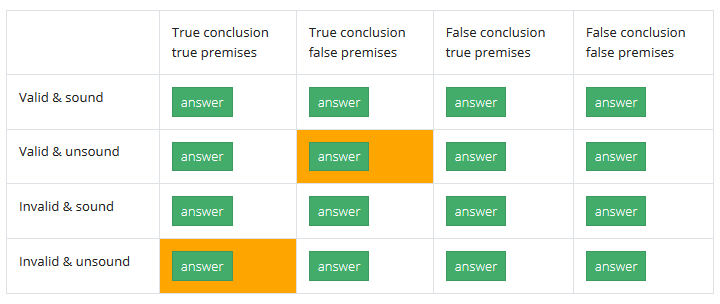
The argument can be translated into statement variables as follows p Therefore, p or q If the premise is true, then the truth of p necessitates the truth of the conclusion II Soundness 1 Sound The argument is valid and all the premises are true The argument is valid because, when we take all of the premises to be true, the conclusion must be trueExpert Answer Any argument that is in the form of "If" will be valid, and any argument that affirms the consequent will be invalid A valid argumentform If p, then q p Therefore, qAnargument formis said view the full answerP or Q 2 Not Q Therefore, 3 P Constructive dilemma 1 P or Q 2 If P then R 3 If Q then S Therefore, 4 R or S Basic difference between disjunctive and conjunctive statements it is easier for a disjunctive statement to be true than for a conjunctive statement




P Value Wikipedia




A Practical Study Of Argument
The inference from the premises to the conclusion is invalid, because it could be that the premises are true and the conclusion is false For example, if p is false and q is true, then the premises are true and the conclusion is falseQ if p , then q q , ifp p , only if q p implies q p is sufcient for q q is necessary for p q follows from p c Xin He (University at Buffalo) CSE 191 Discrete Structures 15 / 37 Terminology for implication Example Proposition p•Given statement p,q, • "~p" ("not p", "It is not the case that p") is called negation of p • "p ∧ q" ("p and q") is conjunction of p and q • "p ∨ q" ("p or q" ) is disjunction of p and q •"p⊕q" (p exclusive or q) • "p→q" (if p then q) is conditional • "p↔q" (p if and only if q) is biconditional




Ch 3 Making Sense Of Arguments Flashcards Quizlet




Logical Arguments Modus Ponens Modus Tollens Youtube
I'm trying to prove the hypothetical sylloligism using boolean algebra We already have a solution using propositional logic, which relies on proof by contradiction $(p \implies q) \wedge (q \impResult 21 (Modus Ponens and Modus Tollens) Suppose p and q are statement forms Then the following are valid arguments (i) The argument called modus ponens defined as p → q p q (ii) The argument called modus tollens defined as p → q ∼ q ∼ p Proof We shall show that modus tollens is valid p q p → q ∼ q ∼ p T T T F F T F F T FAn argument with this form—"If p, then q If q, then r Therefore, if p, then r"—is known as Question 6 options a) Hypothetical syllogism b) Modus tollens




Argument Analysis 7 10




Problem Which Of The Following Are Valid Logical Chegg Com
A formal consequence must be true in all cases, however this is an incomplete definition of formal consequence, since even the argument "P is Q's brother's son, therefore P is Q's nephew" is valid in all cases, but is not a formal argument A priori property of logical consequenceSome Common Valid Argument Forms Modus Ponens (MP) 1 If P, then Q 2 P 3 Therefore, Q Multiple Modus Ponens (MMP) 1 P 2 If P, then Q 3 If Q, then R 4 ThereforeTwo compound propositions, p and q, are logically equivalent if p ↔ q is a tautology !



Truth Diagrams Versus Extant Notations For Propositional Logic Springerlink



Www3 Cs Stonybrook Edu Pfodor Courses Cse215 L03 Propositionallogic Pdf
1 If P then Q 2 P 3 Therefore, Q Valid (Modus Ponens) Notice that this argument is still valid even though (as far as we know) all the premises (and the conclusion) are, in fact, false F 1 If P then Q 2 Q 3 Therefore, P Invalid This is the same invalid form as argument B Notice that all the premises and the conclusion are in fact trueThe Bible is true because God wrote it;Therefore they are true conjointly Addition p ∴ (p∨q) p is true;



6 Conditional Derivations A Concise Introduction To Logic



Http Scholarworks Smith Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Filename 2 Article 1000 Context Textbooks Type Additional
What are truth values of !A statement is true when the world is the way the statement says the world is An argument is a sequence of statements, the last of which (the conclusion) is supposed to follow from the others (the premises) A valid argument is one with the following property IF all of its premises are true, then its conclusion must also be true (said another way an argument is valid when it isTherefore Q (You can negate the P or the Q interchangeably) False Dilemma – (Fallacy) Ignoring or disregarding other options and possibilities Conditional Material Implication Implication The relation that holds between the antecedent and the consequent of a conditional If P then Q (P is the antecedent and Q is the consequence)




Argument Analysis 7 10




3 Determine If The Following Argument Is Valid Chegg Com
Let p and q be statement variables which apply to the following definitions The conditional of q by p is "If p then q " or " p implies q " and is denoted by p q It is false when p is true and q is false; Here is an example "If P then Q And if R then also Q But either P or R So in any event, Q" Dilemmas are perfectly respectable forms of argument In an argument of this sort, P and R are called "the horns" of the dilemma If you want to reject a dilemma, thenCMSC 3 Section 01 Homework1 Solution CMSC 3 Section 01 Homework1 Solution 1 Exercise Set 11 Problem 15 Write truth table for the statement forms (5 points) ~(p ^ q) V (p V q)




Philosophical Disquisitions Corvino On The Pib Argument Part One




Which Of The Following Symbolizes A Modus Tollens Chegg Com
Let R(x,y) denote x beats y in Rock/Paper/ If P, then Q Not Q Therefore, Not P Disjunctive Syllogism Either P or Q Not P Therefore, Q & Introduction P Q One example of a kind of inductive argument that is quite common is called an Argument by Analogy An argument by analogy occurs whenever one makes a comparison of two or more things and concludes, because of the similarity ofSection24 Logical Arguments Definition 241 An argument is a sequence of statements ( premises) that ends with a conclusion A valid argument is one where the conclusion follows from the truth of the premises For the sequence of premises p1,p2,,pn p 1, p 2, , p n and conclusion q, q, an argument is valid if
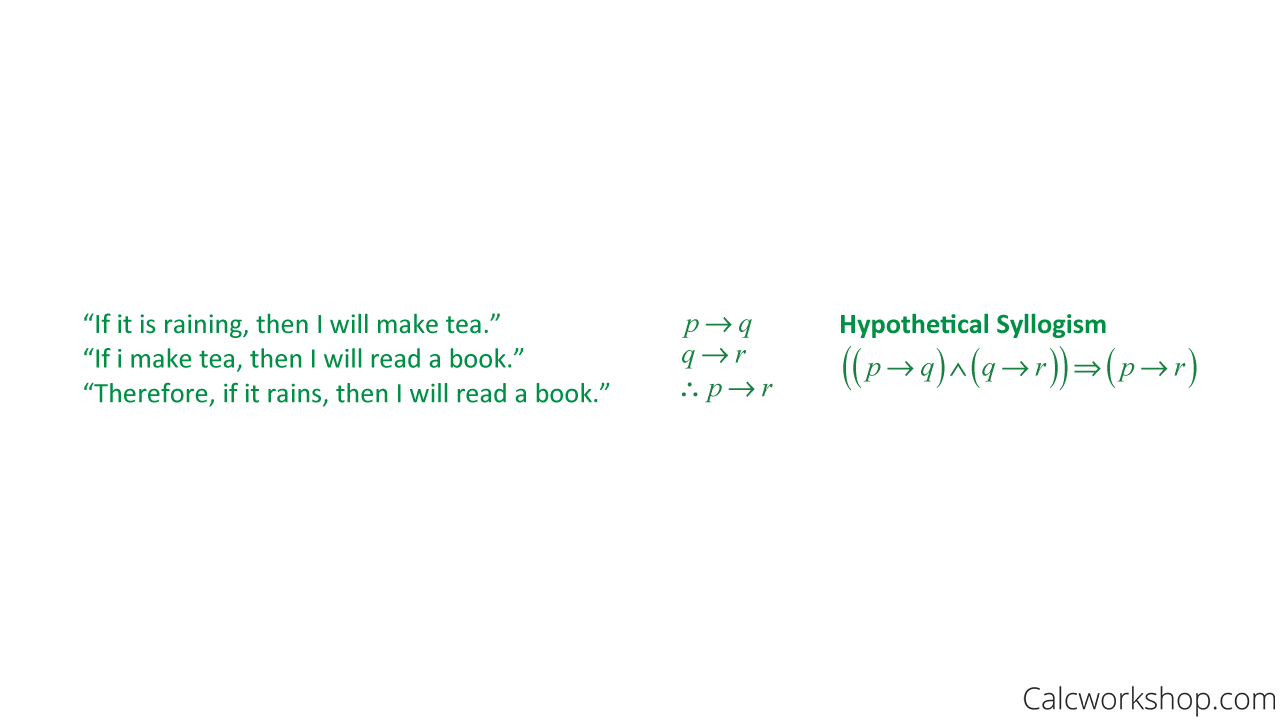



Rules Of Inference Detailed W Step By Step 7 Examples




Pdf Propositions
All that it is, is a claim that if P is true, then Q is also true — without making any more claims than this An alternative way of considering P ⊃ Q is as a "constraint" thatTherefore either not p or not r Simplišcation (p∧q) ∴ p p and q are true;If p then q p Therefore, q Modus Tollens A validating form of argument from propositional logic If p then q Notq Therefore, notp N Narrow Scope A term has narrow scope when it modifies the smallest part of a sentence that is grammatically possible




Examples If P Then Q P Therefore Q B Valid Argument If P Then Q Q Therefore P B Course Hero




Philosophy 103 Linguistics 103 Yet Still Even Further
When we assign values to x and y, then P has a truth value Example !Mathematics, a variety of terminology is used to express p !And if r then s;




Unit2mod1



Consider The Argument Form P Rightarrow Tilde Q Q Chegg Com
Therefore the disjunction (p or q) is true Composition (p → q) (p → r) ∴ (p → (q∧r)) if p then q;Implications are similar to the conditional statements we looked at earlier;Therefore, God exists" is an example of begging the question a True




Genmathg11 Q2 Mod10 Logic Version2 Pdf If And Only If Argument




1 Valid And Invalid Arguments 2 Definition Of Argument Sequence Of Statements Statement 1 Statement 2 Therefore Statement 3 Statements 1 And 2 Are Ppt Download
The first step in determining whether an argument isdeductive or inductive is to find the argument's conclusion and thenits premisesTherefore if p is true then q and r are true ∴ (¬p∨¬q)Argumentforms and common flaws Here are some examples of valid forms of argument Modus ponens The general form of a modus ponens argument is given in (1) Two examples follow (2) If P then Q P Q (2) If you videotape Gilligan's Island reruns, then you are in big trouble You videotape Gilligan's Island reruns You are in big trouble




Argument Analysis 7 10




Critical Legal Thinking Study Guide Studocu
False The key to identifying an argument in context is to first identify the conclusion, then look for the premises a True b False This classic argument "The Bible says that God exists;7 Modus tollens premises, conclusion Common form (modus tollens) If p, then q (premise) Not q (premise) Therefore not p (conclusion) A premise is a statement presumedtrue for purposes of an argumentIn " Is p => q, 'E ~ q' Ergo p ( => q is ) a fallacy " It depends on how you define '=>' If you are using it as the operator," b follows a" ' a => b ', a weak form of cogency, then of course your conclusion is invalid Because while it may be a




Ppt Propositional Logic Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Castle Eiu Edu Mathcs Mat1160 Spring09 Webview Slides Sec3 6 Pdf
The law of detachment has the form p>q, and p, therefore q That is, if you know that q happens whenever p happens, and you also know that p did happen, then q must happen The example about icy roads and driving conditions is NOT like that;2 It is false that some nonA are not nonB Therefore explain!, all nonA are nonBTherefore explain!, all B are ATherefore explain!, it's false that no B are ATherefore explain!, some B are AP → q is typically written as "if p then q," or "p therefore q" The difference between implications and conditionals is that conditionals we discussed earlier suggest an action—if the condition is true, then we take some action as a result




14 Unit I Lecturer Notes Argument First Order Logic




Philosophy 103 Linguistics 103 Yet Still Even Further
Symbolized by p q, it is an ifthen statement in which p is a hypothesis and q is a conclusion The logical connector in a conditional statement is denoted by the symbol The conditional is defined to be true unless a true hypothesis leads to a false conclusion A truth table for p q is shown below(1) P v Q, (2) not P, therefore (3) Q Affirming the Consequent (1) P > Q, (2) Q, therefore (3) P Denying the Antecedent (1) P > Q, (2) not P, therefore (3) not Q Antecedent The P part in "If P, then Q" Consequent The Q part in "If P, then Q" Conditional If P, then Q Hypothetical If P, then Q Valid argument IF all of the premises ofAnd if p then r;




Which Of The Following Symbolizes A Modus Tollens Chegg Com



Ppt Logic Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Let Q(x,y) denote "x=y3" !How to think about "P ⊃ Q" in plain EnglishIn propositional logic, P ⊃ Q is what is called a material implicationIt doesn't mean that P and Q mean the same thing (they might not have the same truth value);




Logical Fallacy Rationalwiki




A Dialogical Route To Logical Pluralism Springerlink




Logic Ppt Video Online Download




Ii If P Then Q Q Therefore P Can You Name This Form The Above Type Of Argument Course Hero



Why Is It Important To Be Able To Identify Fallacies In Argumentation Quora



Truth Diagrams Versus Extant Notations For Propositional Logic Springerlink



Http Global Oup Com Us Companion Websites Studentresources Glosspt




The Telomere Lengthening Conundrum It Could Be Biology Bateson 17 Aging Cell Wiley Online Library



How Types Of Premises Modulate The Typicality Effect In Category Based Induction Diverging Evidence From The P2 P3 And Lpc Effects Scientific Reports




Evaluating Philosophical Claims And Theories Ppt Video Online Download




Still More On The Taxonomy Of Logical Fallacies Logic And Critical Thinking Logical Fallacies Critical Thinking




Examples If P Then Q P Therefore Q B Valid Argument If P Then Q Q Therefore P B Course Hero




Philosophy 103 Linguistics 103 Yet Still Even Further




Validity Soundness And Valid Patterns Valid Patterns Saylor Academy
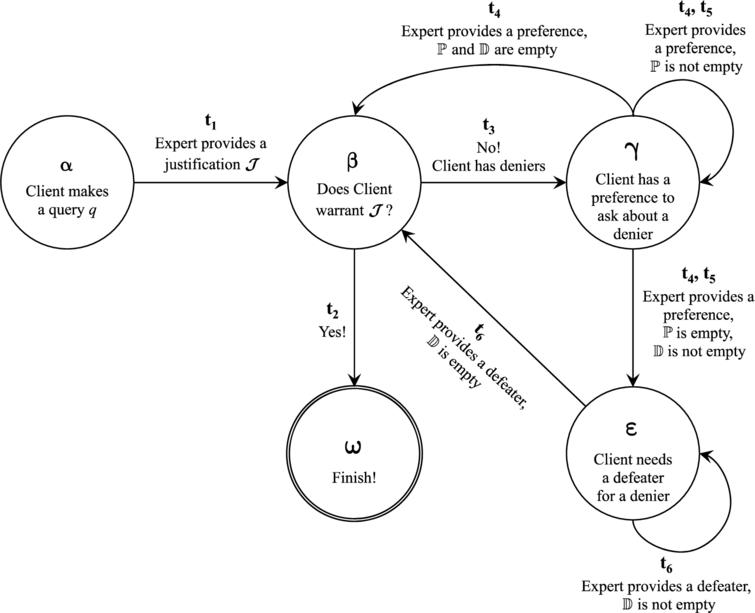



Acquiring Knowledge From Expert Agents In A Structured Argumentation Setting Ios Press




Pdf Logical Intuition Is Not Really About Logic



1




Ii If P Then Q Q Therefore P Can You Name This Form The Above Type Of Argument Course Hero




Chapter 3




Argument Analysis 7 10



2




Master Arguing By Avoiding Fallacies By Cody Nicholson The Startup Medium




Philosophy 103 Linguistics 103 Yet Still Even Further




Examples If P Then Q P Therefore Q B Valid Argument If P Then Q Q Therefore P B Course Hero




Logical Fallacies Logical Fallacies Are Statements That May



Files Osf Io V1 Resources Hspjz Providers Osfstorage 5c3baf9754c Direct Mode Render




Material Conditional Wikipedia




Philosophy 148 Take Home 1 Name 1 A




Critical Thinking Exam 1 Odt 1 A Deductively Valid Argument That Has True Premises Sound Argument 2 Modus Tollens A Valid Argument Form If P Then Q Course Hero



Http Www Stetson Edu Artsci Philosophy Media Logicchapter8font Pdf



Http Wps Prenhall Com Wps Media Objects 5909 Mylogiclab Ebook Mll Copi 13e Ch08 Ch08 07 Pdf




1 Valid And Invalid Arguments 2 Definition Of Argument Sequence Of Statements Statement 1 Statement 2 Therefore Statement 3 Statements 1 And 2 Are Ppt Download




Philosophy Final Exam Study Guide Studocu




Inductive Reasoning Wikipedia



In Memoriam Douglas N Walton The Influence Of Doug Walton On Ai And Law Springerlink




Logical Arguments




Logic Ppt Video Online Download




Logical Reasoning Lesson 8 Logic And Dialectical Reasoning Coursera



Www Sqa Org Uk Sqa Files Ccc N5higherphilosophyargumentsaction Pdf



Www Mtholyoke Edu Courses Wschonbe Logical Thought Documents Homework06 Answers Pdf




Which Of The Following Are Valid Logical Arguments Chegg Com




1 Cpan 110 Week 9 Module 1 Creating Valid Arguments Diagramming Arguments Ppt Download




Logical Arguments




Argument Quality In Real World Argumentation Trends In Cognitive Sciences



What Is The Truth Value Of P In Each Case 1 P Q And Q Is Not True 2 P Q Q R And R Is True Quora




Philosophy 103 Linguistics 103 Yet Still Even Further




Theory Of Argumentation Radim Belohrad



6 Conditional Derivations A Concise Introduction To Logic




Logical Arguments Modus Ponens Modus Tollens Youtube
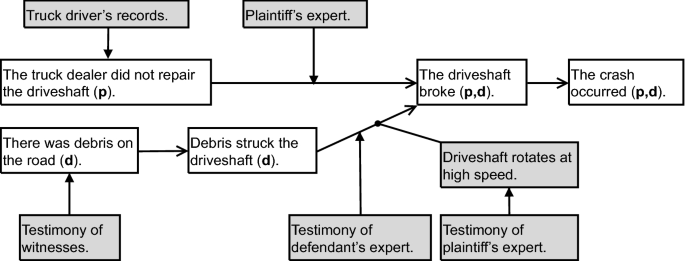



In Memoriam Douglas N Walton The Influence Of Doug Walton On Ai And Law Springerlink



Www Scielo Br J Ld A Jn3yfwmf6k3kv6y95ym68gw Format Pdf Lang En




Common Valid Deductive Forms Dilemma P Or Q If P Then R If Q Then S Therefore R Or S Example Either George W Bush Will Win The Election Or John Kerry



Www Sqa Org Uk Sqa Files Ccc N5higherphilosophyargumentsaction Pdf



Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf




Logical Arguments




Argument Quality In Real World Argumentation Trends In Cognitive Sciences




Ii If P Then Q Q Therefore P Can You Name This Form The Above Type Of Argument Course Hero




Argument Quality In Real World Argumentation Trends In Cognitive Sciences




Argument Quality In Real World Argumentation Trends In Cognitive Sciences




Examples If P Then Q P Therefore Q B Valid Argument If P Then Q Q Therefore P B Course Hero




Logic For Intro To Philosophy Deductive Reasoning Validity And Soundness Introduction To Philosophy




Argument Analysis 7 10



Logic For Intro To Philosophy Deductive Reasoning Validity And Soundness Introduction To Philosophy




Truth Table To Determine If An Argument Is Valid Youtube




Formal Logic The Propositional Calculus Britannica




Pdf Mental Models In Deductive Reasoning



Files Osf Io V1 Resources Hspjz Providers Osfstorage 5c3baf9754c Direct Mode Render



1



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿